
The ERP should match or exceed the required rate of return set by the investor. It’s calculated using the current treasury bill (T-bill) rate or the long-term yield of government bonds. Due to their government backing, these are considered “safe” or “risk-free” investments. Investors are looking for higher returns, but RF is a good number to use as a baseline for cost-of-equity calculations. The amount of equity awarded to investors is determined by a stock price based on the company’s valuation.
Share This Calculator
Unlike public corporations, private companies do not need to report financials nor disclose financial statements. Nevertheless, the owners and private shareholders in such a company can still compute the firm’s equity position using the same formula and method as with a public one. Equity, also referred to as stockholders’ when do you need a certified public accountant or shareholders’ equity, is the corporation’s owners’ residual claim on assets after debts have been paid. As such, many investors view companies with negative equity as risky or unsafe. However, many individuals use it in conjunction with other financial metrics to gauge the soundness of a company.
What Is the Formula for Equity?
- This calculator streamlines the process of determining shareholders’ equity, making it accessible for stakeholders to assess a company’s financial position quickly.
- At some point, accumulated retained earnings may exceed the amount of contributed equity capital and can eventually grow to be the main source of stockholders’ equity.
- Negative shareholder equity means that the company’s liabilities exceed its assets.
- They include investments; property, plant, and equipment (PPE), and intangibles such as patents.
- All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own.
- It aids in understanding the financial health and value of the company.
As per the formula above, you’ll need to find the total assets and total liabilities to determine the value of a company’s equity. All the information required to compute company or shareholders’ equity is available on a company’s balance sheet. The equity of a company is the net difference between a company’s total assets and its total liabilities.
Shareholders Equity Example
Built to help you elevate your game at work, our courses distill complex business topics — like how to read financial statements, how to manage people, or even how to value a business — into digestible lessons. Our library of 200+ lessons will teach you exactly what you need to know to use it at work tomorrow. Shareholders’ equity is adjusted to account for a number of other items found on the balance sheet, including anticipated gains not yet realized and translation on foreign currency. Founded in 1993, The Motley Fool is a financial services company dedicated to making the world smarter, happier, and richer. The Motley Fool reaches millions of people every month through our premium investing solutions, free guidance and market analysis on Fool.com, top-rated podcasts, and non-profit The Motley Fool Foundation. Successful investors look well beyond today’s stock price or this year’s price movement when they consider whether to buy or sell.
Mining and pharmaceutical companies typically have higher Betas, but they also offer higher potential returns for investors. Shareholders’ equity provides investors a glimpse into the financial health of a company. Typically, the higher or more positive a company’s shareholders’ equity is, the more flexibility or financial cushion it has to absorb losses or pay off debt. Share capital, retained earnings, and treasury shares are all reported in the shareholders’ equity section of a balance sheet.
Long-term liabilities are those that are due for repayment in periods beyond one year and include bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations. Stockholders’ equity is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. If a company does not have enough cash flow or assets to cover their liabilities, they are in what is known as “negative equity.” This makes sense as the company’s total stockholders’ equity is the cumulative amount of paid-in capital and retained earnings. Every company has an equity position based on the difference between the value of its assets and its liabilities.
After the repurchase of the shares, ownership of the company’s equity returns to the issuer, which reduces the total outstanding share count (and net dilution). Next, the “Retained Earnings” are the accumulated net profits (i.e. the “bottom line”) that the company holds onto as opposed to paying dividends to shareholders. Shareholders’ equity is the residual claims on the company’s assets belonging to the company’s owners once all liabilities have been paid down.
Negative equity can also occur when there is not enough money realized from sales to cover the company’s debt obligations. Retained earnings grow in value as long as the company is not distributing them to shareholders and only investing them back into the business. Paid-in capital also referred to as stockholders’ funds, is the amount of money that people have invested in a company. Stockholders’ equity is also referred to as shareholders’ or owners’ equity. When companies issue shares of equity, the value recorded on the books is the par value (i.e. the face value) of the total outstanding shares (i.e. that have not been repurchased). Pareto Labs offers engaging on demand courses in business fundamentals.
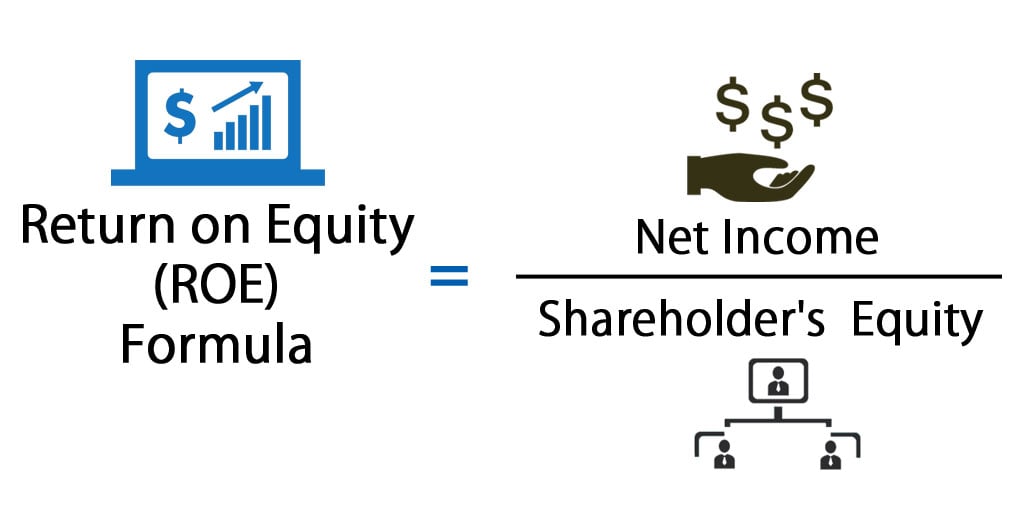
The CAPM formula uses the risk-free rate of return (RF), the expected market rate of return (MRR) for the next year, and the investment’s Beta (β). It uses the current market value (CMV), dividends per share (DPS), and dividend growth rate (GRD). The stockholders’ equity, also known as shareholders’ equity, represents the residual amount that the business owners would receive after all the assets are liquidated and all the debts are paid. Shareholder equity is also known as the book value of the company and is derived from two main sources, the money invested in the business and the retained earnings.
The shareholders’ equity is the remaining amount of assets available to shareholders after the debts and other liabilities have been paid. The stockholders’ equity subtotal is located in the bottom half of the balance sheet. Investors and analysts look to several different ratios to determine the financial company.
JUL
2024

About the Author: